Home > News
-

Announcement
28/03/2025 -

Announcement
01/11/2024 -

Product instrumentally plan
26/09/2022 -

Localization of medica equipment in China
01/06/2022 -

Pulpping Process
20/04/2022 -

NEW Product Intuition 9 Series Controller
11/04/2022 -

Exhibition Plan 2022
22/01/2022 -

Code of Practice for Fresh Water Cooling Towers
02/11/2021 -

Server Immersion Cooling
04/08/2021 -

Tuen Ma Line Commences
07/07/2021 -

Announcement
03/03/2021 -

Link
25/12/2020 -

IWAKI Pumps (Shenzhen) Co., Ltd.
25/05/2020 -

Updated ISO 140001 Cert.
14/02/2020 -

Announcement
02/10/2019
Code of Practice for Fresh Water Cooling Towers 02/11/2021
Code of Practice for Fresh Water Cooling Towers
We would like to share the Code of Practice for Fresh Water Cooling Towers which is drafted by Electrical and Mechanical Services Department, The Government of the HKSAR. The aims of the Code of Practice is providing technical guidelines to prevent any potential risk associated and achieve better/maintain energy efficiency and operational performance of cooling tower system.
Cooling Tower System Important Precautions:
■ Pump(s) is installed for circulating water between the cooling tower and the condenser.
■ Make-up water is required to compensate water losses due to evaporation, drift and bleed-off.
■ Water treatment systems, whether chemical or physical, are essential for a cooling tower system. They should be applied to tackle the problems of corrosion, scale and micro-organism growth, hence to enhance cooling tower water quality.
■ Water meters should be installed to record the total water consumption and the bleed-off volume of cooling tower.
Cooling Water Quality Management
The water treatment programme should aim at controlling the fouling of cooling tower system due to corrosion, scale and microbial growth in order to maintain efficient heat and mass transfer, to ensure free flow of cooling water throughout the system, and to control the proliferation of bacteria in the system.
Water treatment should be maintained throughout the cooling tower system, and also develop an effective water treatment programme.
■ Use two different chemicals alternatively at periodic intervals
■ Use combination of two compatible chemicals to provide better control against a range of micro-organisms
■ Carry out occasional slug dosing to maintain the biocide concentration at a higher level
Regular monitoring of specific water quality parameters can provide an early signal before abnormal condition is detected, which also indicates a potential problem within the system. Below are indicative cooling water quality criteria for fresh water cooling tower:
|
Parameters |
Cooling Water Quality Criteria |
|
Total legionella count |
Less than 10 cfu/mL |
|
Conductivity |
Less than 1500 μS/cm |
|
pH |
4 - 10 |
|
Residual Cl |
0.2 – 1 mg/L (Continuous Dosing) |
|
0.5 – 2 mg/L (Intermittent Dosing) |
|
|
ORP |
400 – 600 mV |
Information shown in the above table is the indicative ranges which may vary with specific cooling tower location and configuration.
Chemical Water Treatment Methods
Chemicals are widely used in cooling tower systems to prevent corrosion, scale formation, and Bacterial and Microbiological Control. Good water quality help to maintain energy efficiency of condenser and heat exchanger.
There are many different types of Corrosion Inhibitor, the working principles of common corrosion inhibitors is enabling a protective film to cover the inside of the cooling water circulation system, preventing corrosive chemical reaction. There should select appropriate corrosion inhibitors for specific system and material used.
Scale is caused by the precipitation of mineral particles in water to form a hard deposit on heating transfer surfaces. The most common type of scaling is formed by carbonates and bicarbonates of calcium and magnesium, as well as iron salts in water. Calcium dominates in fresh water. Scale is caused by the precipitation of mineral particles in water to form a hard deposit on heating transfer surfaces. The most common type of scaling is formed by carbonates and bicarbonates of calcium and magnesium, as well as iron salts in water. Calcium dominates in fresh water. Scale Inhibitor prevent scale formation by keeping the scale forming minerals in solution by dispersing the precipitating substances, so that scale is unable to form. Softener reduce the hardness, alkalinity and solid content of water. Scale forming potential is minimised in acidic environment, therefore, proper pH control is required to provide a suitable environment for both scale and corrosion inhibitors work effectively.
The growth of bacterial and microbiological is one of the major reasons of the deterioration of water quality. Microbiological organisms enter the cooling tower system through make-up water and airborne particulates scrubbed in the cooling tower. Normally, micro-organisms that proliferate in cooling water systems include algae, fungi (yeast and mould) and bacteria. Chemical biocides are the most common products to control the growth of micro-organisms. Different types of biocides should be used together to supplement the deficiency of each other. To dose two types of biocides alternatively can avoid micro-organisms to build up resistance against specific type of biocides. Chemical biocides are including Oxidising Biocide, Non-oxidising Biocide and Biodispersants.
Chemical Dosing
Water treatment chemicals should be added to turbulent zones of cooling tower water system to achieve rapid mixing and well distribution of chemicals. Also, separate dosing point should be used to ensure potentially reactive chemical is diluted prior to adding the second chemical so that no chemical reaction between different chemicals will be occurred to reduce the effectiveness. The dosage concentration of chemicals, including inhibitors and biocides, should be calculated based on the total quantity of water, make-up water quality and bleed-off rate.
A number of chemical dosing methods can be adopted, including:
■ Continuous/intermittent dosing;
■ Proportional dosing related to bleed-off volume;
■ Proportional dosing related to make-up water volume;
■ Dosing controlled by sensor.
Water Treatment System Monitoring
The focus of the entire fresh water cooling tower water treatment is accurate chemical dosing which is varies with water quality. Therefore, the monitoring of the cooling tower cooling water is the key to the water treatment system.
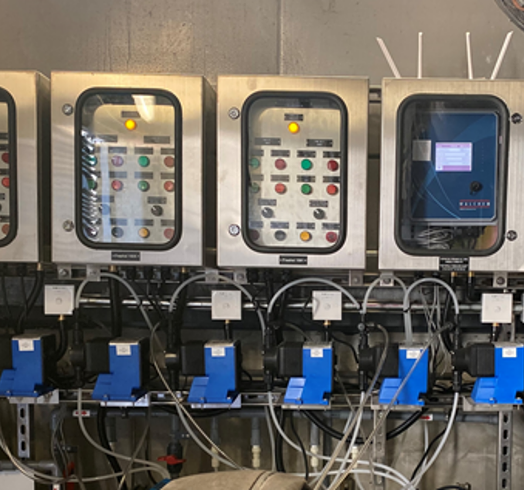
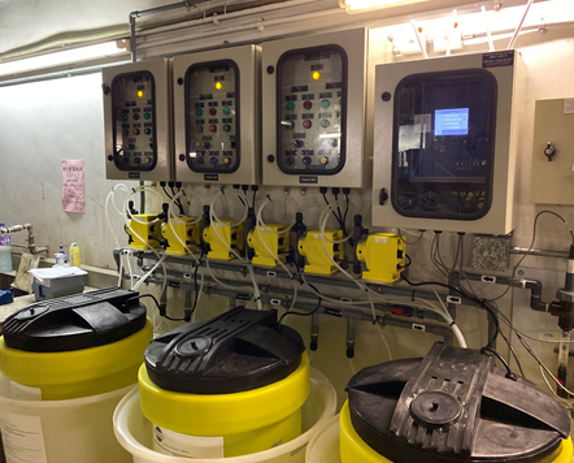
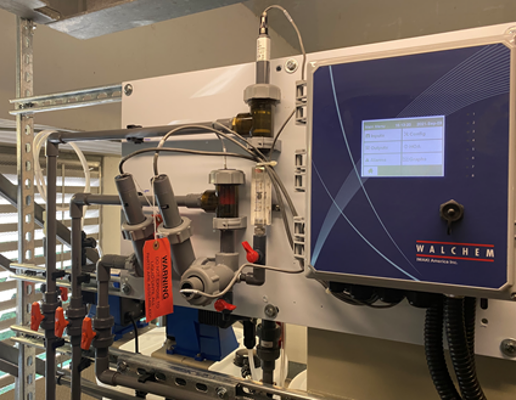
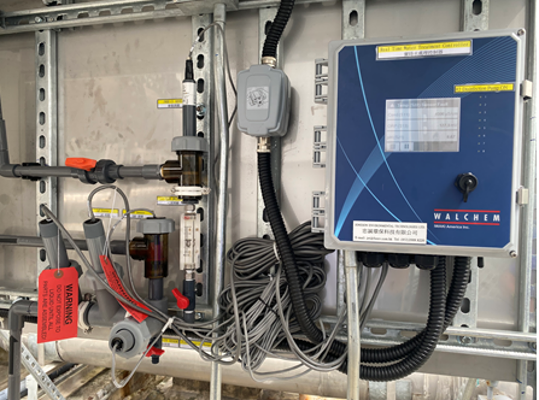
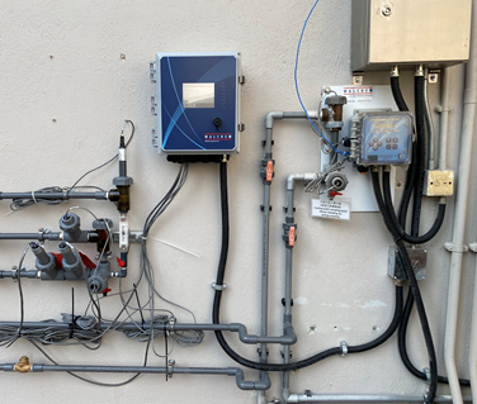
Walchem WCT Series Cooling Tower Controller can act as the central monitoring device, different sensors would feedback the data of water quality automatically, including following:
■ Conductivity
■ Temperature
■ pH/ORP
■ Free chlorine, total chlorine, chlorine dioxide, ozone, peracetic acid, hydrogen peroxide, etc.
Controller would compare the measured data and setup value, then release control signal automatically. Full series Walchem controller is universal sensor input that can adopt almost any type of sensor needed. WCT controller totally provide 2 input slots, 2 virtual inputs, 6 control outputs which is extraordinary flexibility.
Complete flexibility in function of relay including:
■ON/OFF set point
■Time Proportional Control
■Pulse Proportional Control
■Time-base activation
■Lead/Lag Control, etc.
Walchem controller can control IWAKI E series electromagnetic metering pumps directly. Combining with the ET series Tank Unit can form a simple water treatment device easily.
Many different government organizations and public facilities in Hong Kong are already installed WALCHEM WCT900 control device as following:
1. Castle Peak Hospital
2. Pok Oi Hospital
3. Tuen Mun Hospital (2 sets – Main Block and Rehabilitation Block)
4. Fa Yuen Street Municipal Services Building
5. Kowloon Public Library
6. Ko Shan Theatre
7. Lam Tin Complex
8. Kowloon City Delivery Office
9. Kwun Chung Municipal Services Building (2 sets)
10. Food and Environmental Hygiene Department Nam Cheong Offices and Vehicle Depot
11. Hong Kong Velodrome
12. Po Wing Road Sports Centre
13. Shek Wu Hui Municipal Services Building
14. Tiu Keng Leng Public Library
15. Sai Kung Tseung Kwan O Government Complex
16. Yuen Chau Kok Sports Centre
17. Cheung Sha Wan Government Offices
18. Tung Chung Swimming Pool
19. Tung Chung Municipal Services Building
20. Justice Place
21. Lo Wu Control Point
22. Shenzhen Bay Control Point
23. ICAC HQ Building
24.Customs HQ Building
25. Tuen Mun Police Station
26. Hong Kong Police Headquarters
|
|
|
|
Tuen Mun Hospital |
Pok Oi Hospital |
|
|
|
|
Castle Peak Hospital |
Queen Mary Hospital |
|
|
|
|
Ko Shan Threater |
Lam Tin Complex |
|
|
|
|
Fa Yuen Street Municipal Services Building |
Kowloon Public Library |
Please contact IWAKI China for details.








 粤公网安备 44010502002553号
粤公网安备 44010502002553号